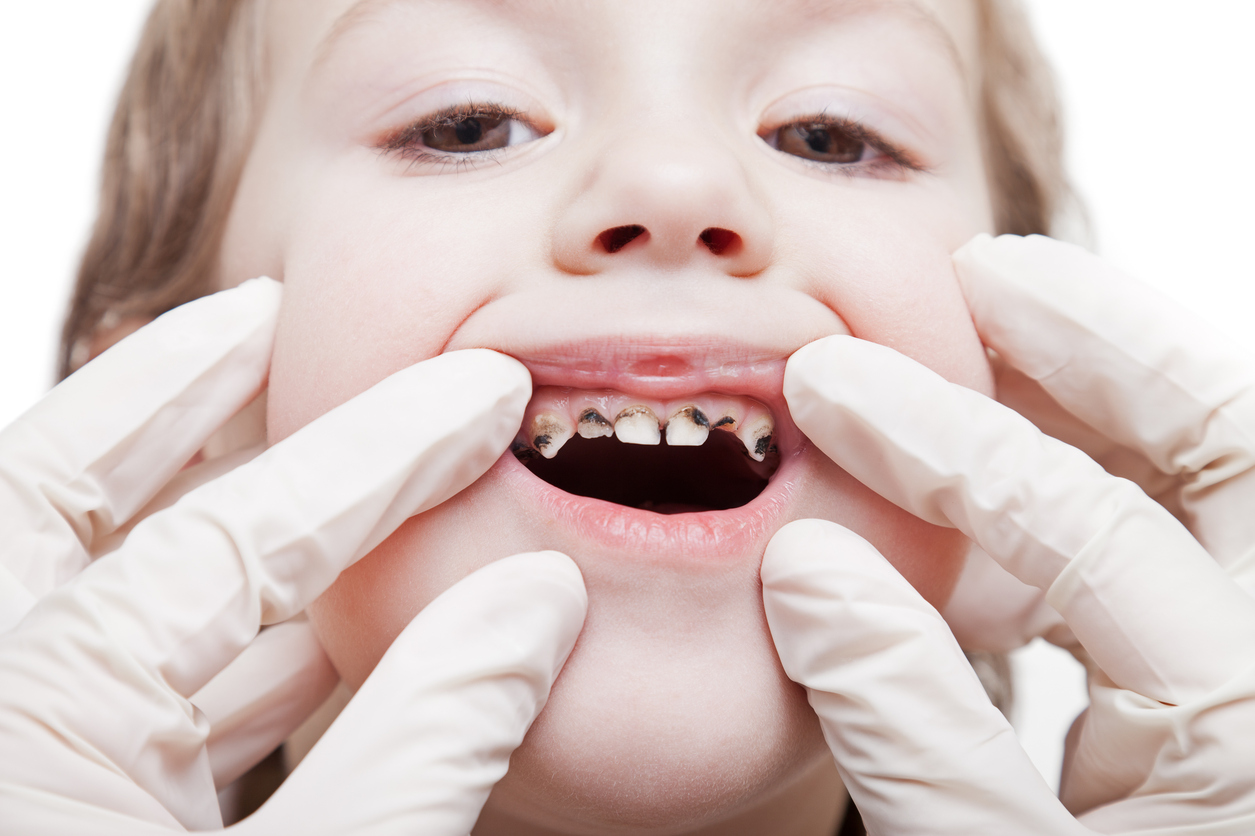
Black spots on teeth can be a source of significant concern for both patients and dental professionals. These spots can vary in their appearance, from small specks to larger patches, and can have a range of underlying causes. As a dentist, understanding the origins of these spots, their implications, and how to manage them is crucial for providing effective patient care. This article delves into the causes, methods for removal, and strategies for prevention of black spots on teeth.
Causes of Black Spots on Teeth
Dental Caries (Cavities):
One of the most common causes of black spots on teeth is dental caries. Caries occur when bacteria in the mouth produce acids that erode tooth enamel. Initially, these spots might appear as white or light-colored, but as the decay progresses and the enamel breaks down, the affected area can turn black. The black coloration is often a result of the accumulation of bacteria, food particles, and staining agents.
Extrinsic Staining:
Extrinsic stains are surface stains caused by the consumption of certain foods and beverages, such as coffee, tea, red wine, and tobacco. These substances contain pigments that can adhere to the enamel and, over time, create black spots. Although these stains are typically more superficial, they can be quite noticeable and distressing to patients.
Intrinsic Staining:
Unlike extrinsic stains, intrinsic staining originates from within the tooth. This can be due to factors such as excessive fluoride exposure during tooth development (fluorosis), certain medications like tetracycline antibiotics, or trauma to the tooth. Intrinsic stains can lead to black spots or dark discolorations that are embedded within the tooth structure.
Dental Restorations:
Occasionally, black spots may appear around dental restorations such as fillings or crowns. This can be due to the accumulation of plaque or tartar around the restoration, which can become stained over time. Additionally, the materials used in some restorations might react with other substances in the mouth, leading to discoloration.
Removal of Black Spots on Teeth
Professional Cleaning:
For extrinsic stains, a thorough professional cleaning by a dentist or dental hygienist is often effective. Techniques such as scaling and polishing can remove surface stains and reveal the natural color of the black spot causes removal dentists guide. In some cases, air abrasion or ultrasonic cleaning might be employed to tackle more stubborn stains.
Whitening Treatments:
If black spots are due to intrinsic staining or if surface stains persist after cleaning, whitening treatments may be necessary. Teeth whitening procedures, including in-office treatments and take-home kits, can help to lighten the overall color of the teeth and reduce the contrast of black spots. It’s important to evaluate the patient’s suitability for whitening treatments and discuss potential risks and benefits.
Restorative Options:
For more severe cases, especially those involving carious lesions, restorative treatments may be required. This could involve removing the decayed portion of the tooth and placing a dental filling or crown. In some instances, a root canal might be necessary if the decay has reached the pulp of the tooth.
Microscopic Analysis:
In cases where the cause of the black spots is unclear, microscopic analysis might be used to determine the nature of the discoloration. This can help in formulating an appropriate treatment plan.
Prevention of Black Spots on Teeth
Oral Hygiene Practices:
The cornerstone of preventing black spots on teeth is maintaining excellent oral hygiene. Patients should be encouraged to brush their teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove plaque and food particles. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are also essential for early detection and management of potential issues.
Dietary Modifications:
Advising patients to limit their intake of staining foods and beverages can help in preventing extrinsic stains. Reducing consumption of coffee, tea, and tobacco products can minimize the risk of developing black spots. Additionally, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and water can support overall dental health.
Fluoride Use:
For individuals at risk of dental caries, the use of fluoride treatments can help strengthen enamel and prevent decay. Fluoride varnishes and supplements can be particularly beneficial for children and individuals with a history of cavities.
Protective Measures:
In cases where intrinsic staining is a concern, protecting teeth from trauma and minimizing the use of staining medications can be beneficial. For patients undergoing orthodontic treatments or other procedures, using protective measures to avoid damage to the enamel is advisable.
Conclusion
Black spots on teeth can be a sign of various dental issues, ranging from superficial staining to more serious conditions like caries or intrinsic discoloration. As a dentist, a comprehensive understanding of the causes, removal techniques, and prevention strategies for these spots is essential for effective patient care. By addressing these issues promptly and implementing preventive measures, dental professionals can help patients maintain healthy, attractive smiles and prevent the recurrence of black spots on their teeth.