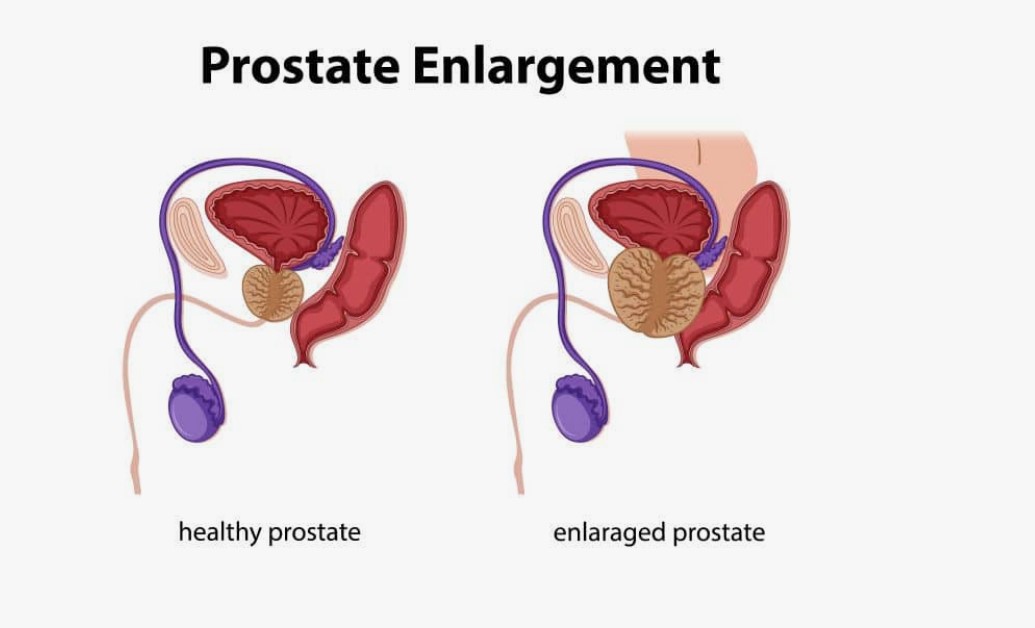
An enlarged prostate, medically known as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a common condition affecting men as they age. The prostate is a small gland located just below the bladder, and it plays a vital role in the male reproductive system by producing fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. As men grow older, the prostate can enlarge, which can lead to various urinary symptoms. Though BPH is not cancerous, it can cause discomfort and impact the quality of life if left untreated.
At Urology Partners of North Texas, the team of specialists provides comprehensive care for men experiencing symptoms of an enlarged prostate, offering both medical and surgical treatments to help manage the condition effectively.
What Causes an Enlarged Prostate?
The exact cause of BPH is not fully understood, but it is thought to be linked to changes in male hormones, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which can accumulate in the prostate and cause it to grow. Other factors that may contribute to the development of an enlarged prostate include:
- Aging: BPH is most commonly seen in men over the age of 50. As men age, the balance of hormones in their bodies changes, which may cause the prostate to enlarge.
- Family History: Genetics can play a role in the likelihood of developing BPH. If men in your family have had an enlarged prostate, you may be at higher risk.
- Lifestyle Factors: A sedentary lifestyle, obesity, and lack of physical activity may increase the risk of BPH. Conversely, regular exercise and a healthy diet may help reduce the risk.
Symptoms of an Enlarged Prostate
The symptoms of an enlarged prostate vary, and not all men with BPH will experience severe issues. However, as the prostate enlarges, it can press against the urethra (the tube that carries urine out of the body), making it more difficult for urine to flow. Common symptoms of an enlarged prostate include:
- Frequent Urination: Men with BPH may find themselves needing to urinate more often, especially at night (nocturia).
- Urgency to Urinate: A sudden and strong need to urinate, often accompanied by difficulty in holding it, is a common symptom.
- Weak Urine Stream: Men may notice that their urine stream is weaker or that it takes longer to start or finish urinating.
- Incomplete Emptying: Feeling like the bladder isn’t completely empty after urination is another common symptom of BPH.
- Dribbling at the End of Urination: Men with BPH may experience dribbling or leakage of urine after they have finished urinating.
In some cases, BPH can lead to more severe complications such as urinary tract infections, bladder stones, or even kidney damage if the condition is left untreated. Visit: kinkedpress.com
Diagnosing an Enlarged Prostate
If you are experiencing symptoms of an enlarged prostate, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation. At Urology Partners of North Texas, the diagnosis of BPH typically begins with a medical history and physical examination, which includes a digital rectal exam to assess the size of the prostate.
In addition to the physical exam, other tests may be used to confirm the diagnosis and evaluate the severity of the condition. These tests may include:
- Urine Test: A urinalysis can help rule out infections or other conditions that may cause similar symptoms.
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: PSA levels are often measured to screen for prostate cancer, as BPH and prostate cancer can cause similar symptoms.
- Ultrasound or MRI: Imaging tests can provide a more detailed look at the prostate and surrounding organs.
- Urodynamic Testing: This test assesses how well the bladder and urethra are functioning during urination.
Treatment Options for an Enlarged Prostate
The treatment for BPH depends on the severity of the symptoms and how much they impact the patient’s daily life. Some men with mild symptoms may not require immediate treatment but will need regular monitoring to ensure that the condition doesn’t worsen. For others, medication or surgery may be necessary.
- Medications:
- Alpha Blockers: These medications help relax the muscles in the prostate and bladder neck, making it easier to urinate. They are effective in relieving symptoms quickly.
- 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors: These drugs work by shrinking the prostate over time, helping to relieve symptoms and prevent further growth.
- Combination Therapy: In some cases, a combination of alpha blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors may be prescribed for greater effectiveness.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: For men who do not respond to medication or have more severe symptoms, there are minimally invasive procedures available. These procedures are designed to relieve pressure on the urethra and improve urine flow without the need for major surgery. Examples include:
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): This procedure involves removing part of the prostate that is blocking the flow of urine.
- Laser Therapy: High-energy lasers are used to destroy excess prostate tissue and relieve symptoms.
- Surgical Treatment: In more advanced cases of BPH, surgery may be necessary to remove or reduce the size of the prostate. Surgery is typically reserved for men with severe symptoms or complications like urinary retention, recurrent infections, or bladder stones.
Managing and Preventing Symptoms
While BPH is not entirely preventable, there are steps men can take to reduce the risk of developing symptoms or managing them once they arise. Some helpful lifestyle changes include:
- Stay Active: Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and improve urinary function.
- Limit Fluid Intake in the Evening: This can reduce nighttime urination and help improve sleep.
- Avoid Caffeine and Alcohol: Both can irritate the bladder and worsen symptoms.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can support prostate health.
If you are experiencing symptoms of an enlarged prostate, it’s important to seek medical advice to manage the condition effectively. For more information on BPH and treatment options, visit www.upnt.com.