Polycystic Kidney Disease Market Outlook
The high prevalence of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), affecting 1 in every 400 to 1,000 individuals worldwide, is a key factor driving the drug development pipeline. In the United States, around 500,000 people are affected by this common genetic condition. Polycystic Kidney Disease Drug Pipeline Analysis This widespread impact highlights the critical need for better treatments, motivating pharmaceutical companies and research institutions to innovate and expand the pipeline, providing new hope for patients with ADPKD.
Get a Free Sample Report with a Table of Contents: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/clinical-trials/polycystic-kidney-disease-drug-pipeline-analysis/requestsample
Polycystic Kidney Disease: Introduction
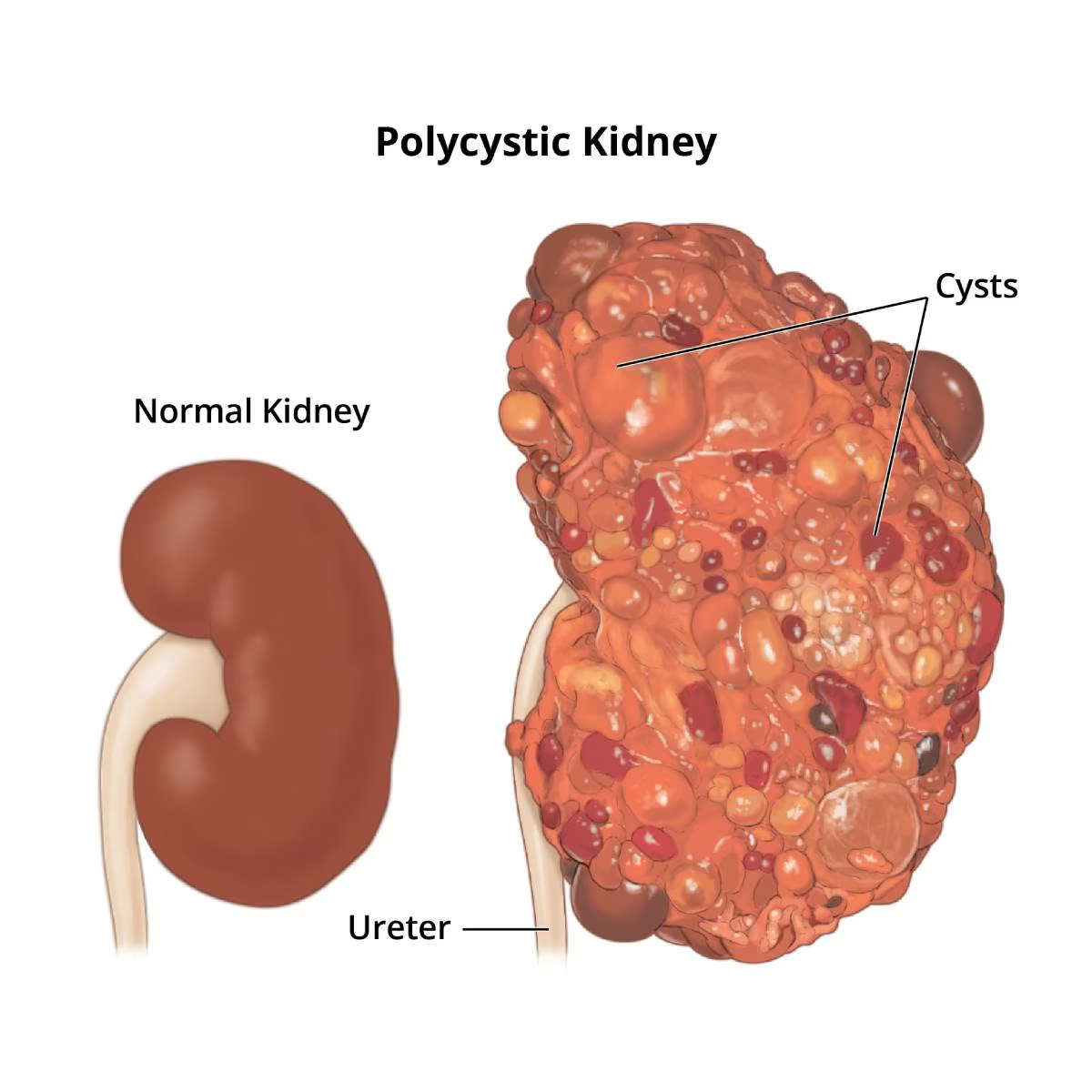
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder characterised by the growth of numerous cysts in the kidneys, which can lead to kidney enlargement and impaired function over time. Symptoms often include high blood pressure, abdominal pain, and kidney failure in advanced stages. The disease can develop gradually, with early signs often overlooked. There are two main types: autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive. Treatment options aim to manage symptoms and slow progression, with ongoing research focused on developing therapies to prevent cyst growth and improve kidney function in affected individuals. Early diagnosis is crucial for better management and outcomes.
Polycystic Kidney Disease Overview
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) leads to the development of fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys, which can impair kidney function over time. The condition is often genetic, with two major forms: autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive. Symptoms include high blood pressure, abdominal pain, and kidney enlargement, which progressively worsens.
Treatment options focus on managing symptoms and slowing cyst growth. The most common therapy is the use of vasopressin receptor antagonists like tolvaptan, which helps reduce cyst enlargement. Additional treatments include blood pressure control, pain management, and potential kidney transplantation in severe cases.
Read Full Report with Table of Contents: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/clinical-trials/polycystic-kidney-disease-drug-pipeline-analysis
Drug Pipeline Therapeutic Assessment
Analysis by Route of Administration
1. Oral
2. Parenteral
3. Topical
Analysis by Phase
1. Preclinical Phase
2. Phase I
3. Phase II
4. Phase III
5. Phase IV
Analysis by Drug Class
1. Recombinant Fusion Proteins
2. Small Molecule
3. Monoclonal Antibody
4. Peptide
5. Polymer
6. Gene Therapy
7. Kinase Inhibitor
Polycystic Kidney Disease Drug Classes
Polycystic kidney disease treatments utilise a range of drug classes, each designed to target specific pathways and mechanisms involved in cancer growth and survival. These diverse classes enhance the effectiveness of therapy and contribute to personalised treatment strategies. Understanding these drug classes is essential for optimising patient outcomes.
1. Recombinant Fusion Proteins
Recombinant fusion proteins are engineered proteins that combine the functionalities of multiple molecules. These drugs target and modify specific pathways involved in cyst growth and kidney function. In PKD, they may help reduce cyst size or slow kidney damage by influencing cellular processes in the kidneys.
2. Small Molecule
Small-molecule drugs are chemical compounds designed to modulate specific biochemical pathways. In PKD, these drugs can target signalling pathways that contribute to cyst formation and growth. They may also help reduce cyst enlargement or slow kidney deterioration, offering patients oral treatment options.
3. Monoclonal Antibody
Monoclonal antibodies are particular immune proteins targeting certain antigens involved in disease progression. For PKD, monoclonal antibodies aim to interfere with pathways that promote cyst growth or kidney fibrosis. These therapies are being explored for their potential to slow the disease and improve renal function.
4. Peptide
Peptide-based therapies consist of short chains of amino acids designed to modulate cellular activities. In PKD, peptides may be developed to target specific receptors or pathways associated with cyst formation and kidney damage. These therapies can offer a more targeted and less invasive approach to managing the disease.
5. Polymer
Polymer-based drugs use engineered polymers to improve the delivery and stability of therapeutic agents. In PKD, polymers may be used to enhance the bioavailability of drugs or help deliver targeted therapies directly to the kidneys. This approach improves the efficiency and safety of treatments while minimising systemic side effects.
6. Gene Therapy
Gene therapy for PKD aims to address the root cause by introducing functional genes into kidney cells. This innovative approach seeks to correct genetic defects or slow cyst formation, offering potential long-term benefits. Gene therapy holds promise as a curative treatment, potentially halting or reversing kidney damage.
7. Kinase Inhibitor
Kinase inhibitors target specific enzymes (kinases) involved in cell signalling pathways that regulate cell growth and division. In PKD, these inhibitors may help reduce cyst growth or prevent kidney fibrosis by modulating these pathways. This class of drugs is being explored for its potential to slow disease progression and preserve kidney function.
Polycystic Kidney Disease– Pipeline Drug Profiles
This section provides an overview of the various drugs used in the treatment of polycystic kidney disease. It covers their classifications, mechanisms of action, and methods of administration, offering essential insights for effective treatment strategies.
1. RGLS8429
RGLS8429 is an RNA-based therapy currently under development for PKD. It targets specific RNA molecules to modulate the pathways responsible for cyst growth. In preclinical studies, RGLS8429 has shown promise in reducing cyst enlargement and improving kidney function. This novel approach may offer a breakthrough in treating PKD and slowing disease progression.
2. Tolvaptan
Tolvaptan is a vasopressin receptor antagonist approved for treating PKD. It works by blocking the action of vasopressin, a hormone that promotes cyst growth in the kidneys. Clinical studies have demonstrated that tolvaptan can slow the progression of kidney damage in patients with PKD, improving long-term outcomes and delaying the need for dialysis.
3. AL01211
AL01211 is a drug currently being explored for PKD, aimed at targeting key pathways involved in cyst formation. It works by inhibiting specific enzymes that drive cyst growth and kidney enlargement. Early clinical trials suggest it may significantly reduce cyst size and protect kidney function, offering hope for patients with advanced PKD.
Polycystic Kidney Disease: Competitor Landscape
The key features of the report include patent analysis, clinical trials, grants analysis, funding and investment analysis, partnerships, and collaborations analysis by the leading key players. The major companies in the market are as follows:
Palladio Biosciences
Palladio Biosciences, based in Durham, North Carolina, is dedicated to developing novel therapies for rare kidney diseases, including PKD. Their research focuses on RNA-based therapeutics, such as RGLS8429, which aims to address the underlying genetic mechanisms of cyst formation and improve kidney function, offering new treatment options for PKD patients.
Regulus Therapeutics Inc.
Regulus Therapeutics, headquartered in San Diego, California, focuses on RNA-targeted drug development. Their lead compound, RGLS8429, targets specific RNA molecules involved in PKD, offering a potential new class of therapy to slow cyst growth and preserve kidney function. Regulus aims to transform the treatment landscape for PKD with innovative genetic-based therapies.
Novartis Pharmaceuticals
Novartis Pharmaceuticals, a global leader in healthcare, has developed tolvaptan, a leading treatment for PKD. Their continued research into kinase inhibitors and gene therapies aims to expand treatment options and improve outcomes for PKD patients. Novartis’s dedication to innovation is at the forefront of advancing therapies for kidney diseases, including polycystic kidney disease.
Other key players in the landscape include Kadmon Corporation, LLC, Pfizer, Otsuka Pharmaceutical Development & Commercialization, Inc., Rege Nephro Co., Ltd., AceLink Therapeutics, Inc., Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated, Advice Pharma Group srl.
We at Expert Market Research always strive to provide you with the latest information. The numbers in the article are only indicative and may be different from the actual report.