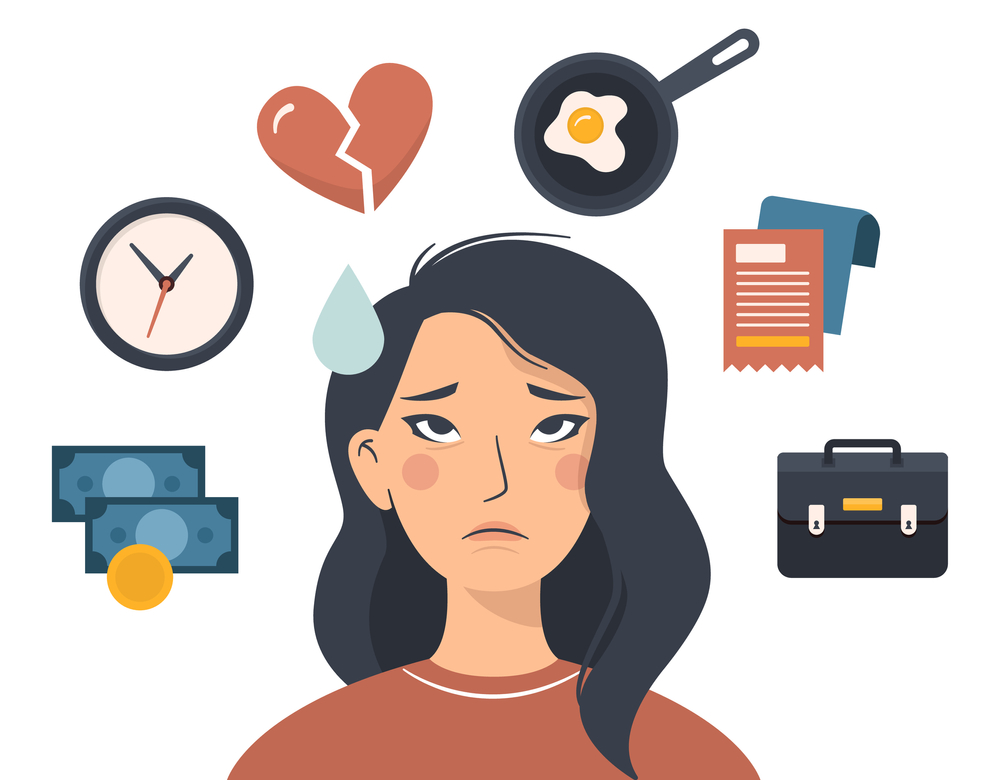
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a significant mental health condition marked by ongoing feelings of sorrow, despair, and a loss of interest in everyday life. Physical health also plays a crucial role in mental well-being. Individuals who neglect their physical health are at a higher risk of developing mental health issues such as depression. In addition, poor lifestyle habits can hinder recovery from depressive episodes, as they may undermine the effectiveness of treatment.
This blog will discuss how certain lifestyle factors and environmental triggers can increase the risk of major depressive disorder.
Negative Lifestyle Factors that Contribute to Major Depressive Disorder
Certain negative lifestyle factors can significantly impact mental health, often leading to the onset or worsening of depression. When habits and routines fail to support emotional and physical well-being, they can create a cycle that is difficult to break. By recognizing these behaviors, individuals can take proactive steps to improve their overall mental health and reduce the risk of developing or prolonging depressive episodes.
- Substance Abuse: Excessive use of drugs and alcohol can significantly affect mood and mental health, increasing the likelihood of depression.
- Overwork: Chronic stress and overworking can lead to burnout, which can contribute to depressive symptoms.
- Poor Diet: Diets high in caffeine, sugar, and processed foods can disrupt mood regulation and overall mental health.
- Lack of Physical Activity: A lifestyle with no physical activity is linked to an increased risk of depression.
- Inadequate Sleep: Poor sleep patterns or sleep deprivation are strongly associated with depressive symptoms.
- Limited Leisure & Social Activities: A lack of time for fun, recreation, and socializing can lead to feelings of isolation and contribute to depression.
These are a few reasons why negative lifestyle factors can increase the onset of major depressive disorder.
Environmental Triggers of Depression
In addition to lifestyle factors, various environmental triggers can also play a significant role in the onset of major depressive disorder. These triggers often come from pollutants and other environmental stressors that affect our health, both physically and mentally.
The following are examples of environmental factors that can influence depression:
- Chemical Pollution: Our bodies are constantly exposed to synthetic chemicals such as food additives, preservatives, pesticides, hormones, drugs, and industrial byproducts. These chemicals, present in our air, water, and food, can negatively impact our mental health.
- Noise & Electrical Pollution: Other environmental stressors, such as noise pollution and electrical pollution, can also contribute to mental health issues. Noise pollution, common in urban environments, can cause anxiety, irritability, and sleep disturbances, all of which may contribute to depressive symptoms. Similarly, electrical pollution, caused by the radio waves generated by modern electronic devices, has been linked to mood disturbances.
- Environmental Disasters: Natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, or tsunamis can trigger depression in individuals already vulnerable to the condition. Even people who might not have a strong predisposition to depression can develop symptoms after experiencing a catastrophic event, such as losing their home to a natural disaster. The emotional toll of such events, coupled with the stress and uncertainty they bring, can be significant contributors to mental health challenges.
Managing Major Depressive Disorder
Although it is impossible to control all environmental factors, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize exposure to harmful influences. By adopting healthier lifestyle habits and being mindful of environmental triggers, one can significantly reduce the risk of developing depression or better manage existing symptoms. These intentional changes can play a crucial role in improving overall mental health and well-being.
The Role of Social & Relationship Factors in Managing Major Depressive Disorder
Social Isolation and loneliness are key contributors to depression, particularly in today’s fast-paced, disconnected world. Individuals who lack meaningful relationships or social support are more likely to experience feelings of loneliness and isolation, which can increase the risk of developing this condition. Humans are inherently social creatures, and the absence of positive, nurturing relationships can leave a person feeling disconnected and emotionally unsupported. Research has shown that social isolation can lead to changes in brain chemistry and function that make a person more susceptible to depressive symptoms.
Chronic Stress from ongoing life difficulties, such as financial struggles, job instability, or family issues, can also be a major trigger for major depressive disorder. The constant pressure of dealing with such stressors can wear down an individual’s coping mechanisms, leading to emotional exhaustion and feelings of helplessness. When these stressors become chronic, they can have a lasting effect on mental health, creating a vicious cycle where stress and depression reinforce each other. Furthermore, the constant barrage of negative news, the pressure to succeed, and the expectation to maintain a “perfect” lifestyle in the age of social media can further amplify feelings of inadequacy and anxiety, deepening the depressive state.
How Positive Support Can Help Overcome Major Depressive Disorder
Positive social support can have the opposite effect, helping individuals buffer the impacts of stress and protecting against this condition.
- Strong, healthy relationships, whether with family, friends, or a support network, can provide emotional stability, a sense of belonging, and the encouragement needed to cope with difficult situations.
- Engaging in community activities, seeking therapy, or joining support groups can help foster social connections that promote mental well-being.
- Moreover, healthy communication skills and conflict resolution strategies can improve interpersonal relationships, reducing the likelihood of relational stress contributing to major depressive disorder.
Read Also: Awake and Empowered: Tackling Obstructive Sleep Apnea with Revolutionary Treatments
Conclusion
Recognizing the impact of lifestyle, environmental, and personal factors is essential in managing major depressive disorder. By adopting healthier habits, fostering social connections, and minimizing exposure to negative environmental triggers, individuals can better support those struggling with this condition and improve their overall mental health. Addressing these factors holistically is key in the fight against major depressive disorder. Numerous clinical research organizations are dedicated to not only providing potential treatment options but also creating a safe environment where individuals feel comfortable sharing their experiences. These organizations play a vital role in supporting mental health awareness and helping those affected feel heard and understood. Join their mission today!