While most sebaceous cysts are harmless and can be left alone, there are certain situations where it’s important to see a doctor. Here’s when you should seek medical attention for a sebaceous cyst:
1. Pain or Tenderness
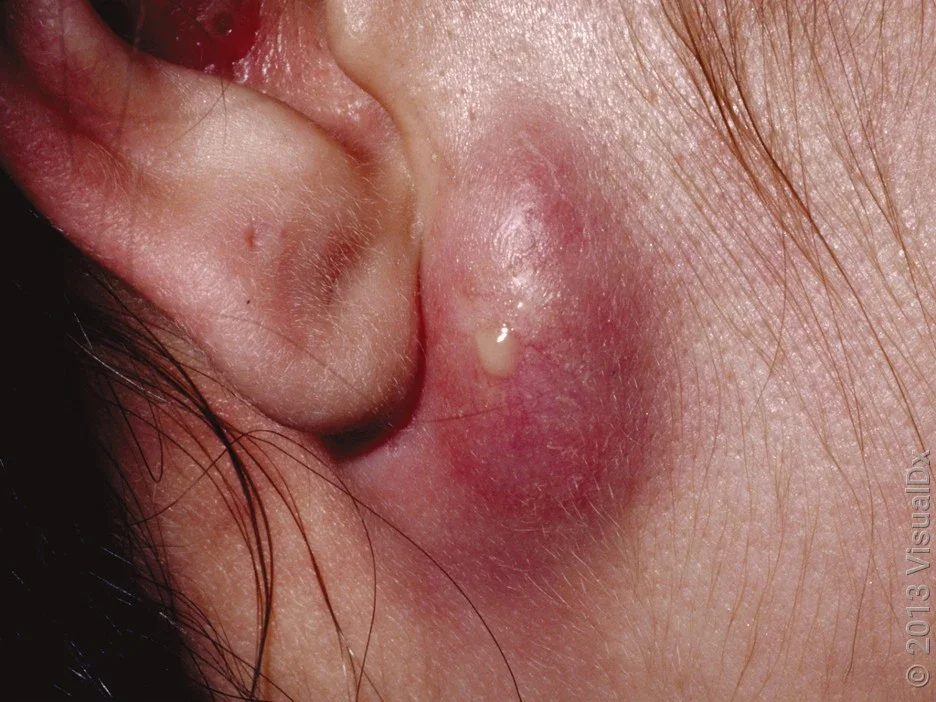
If your sebaceous cyst (عملية الكيس الدهني) becomes painful or tender to the touch, it could be a sign of infection or inflammation. Painful cysts may need medical intervention to relieve discomfort and prevent complications.
2. Signs of Infection
If the cyst becomes red, swollen, warm to the touch, or starts to drain pus or an unpleasant-smelling fluid, it may be infected. Infections can cause serious complications, so it’s important to get it treated promptly. Your doctor may recommend antibiotics or drainage of the cyst.
3. Rapid Growth
If the cyst begins to grow very quickly or unexpectedly, it could indicate an issue that needs medical attention. Rapid growth might sometimes signal that the cyst is becoming infected, or it could be a sign of something more serious (though this is rare).
4. Changes in Appearance
If the cyst changes in color, becomes hard, or feels different from how it originally did, it’s worth having it checked out. In rare cases, cysts can be cancerous, so it’s better to have changes evaluated by a doctor just to be safe.
5. Cyst Becomes Large or Uncomfortable
If the cyst grows to a size where it starts to interfere with your daily activities (e.g., it rubs against clothing or causes discomfort during movement), it may need to be removed. Large cysts are also more prone to infection.
6. Recurrent Cysts
If you’ve had a sebaceous cyst removed but notice it coming back in the same spot, it’s a good idea to consult your doctor. Recurring cysts might require a more thorough removal process to prevent them from reappearing.
7. Cyst Near Sensitive Areas
If the cyst is located on sensitive areas like the face, neck, or genitals, it’s worth seeing a doctor to discuss removal options, as these areas are more prone to infection, scarring, and cosmetic concerns.
8. Concern About Cancer
Although sebaceous cysts are almost always benign, if you’re concerned that your cyst may be something more serious, it’s a good idea to get it checked out. Your doctor can perform tests to rule out cancer or other conditions. If necessary, a biopsy can be done to confirm the diagnosis.
9. Cyst Rupture
If the cyst ruptures or bursts, it can lead to infection or severe irritation of the skin. If this happens, it’s essential to see a doctor to clean the area properly and prevent further complications.
10. Difficulty Moving or Breathing (Rare Cases)
In extremely rare cases, a sebaceous cyst can develop in such a way that it presses on surrounding structures, potentially affecting movement or even breathing. If you experience difficulty breathing or a feeling of tightness near the cyst, seek immediate medical care.
What a Doctor Might Do:
-
Drainage or Incision: If the cyst is infected or causing significant issues, your doctor may drain the cyst or remove it surgically. They will do this in a sterile environment to prevent further infection.
-
Antibiotics: If there’s an infection, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to clear up the infection before performing any procedure.
-
Removal: If the cyst is large, recurrent, or causing problems, your doctor may recommend surgical removal. This typically involves removing the cyst along with its wall to prevent regrowth.
Summary
While most sebaceous cysts are benign and harmless, it’s important to be aware of changes in size, appearance, and symptoms. If you notice any of the signs mentioned above, it’s a good idea to consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and treatment.
Here are some Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about sebaceous cysts:
1. What is a sebaceous cyst?
A sebaceous cyst is a small, non-cancerous bump under the skin that forms when a sebaceous gland or hair follicle becomes blocked. The cyst contains a thick, oily substance called sebum, which is normally produced by the sebaceous glands to lubricate the skin.
2. What causes a sebaceous cyst?
Sebaceous cysts are typically caused by blocked hair follicles or sebaceous glands. The blockage can be due to:
-
Excessive oil production
-
Hormonal changes
-
Trauma to the skin (e.g., a small injury)
-
Genetics (family history)
-
Skin conditions (such as acne or dermatitis)
3. Are sebaceous cysts dangerous?
No, sebaceous cysts are generally benign (non-cancerous) and not dangerous. However, they can become infected, which can cause pain, swelling, and redness, and in some cases, require medical treatment.
4. How can I tell if a sebaceous cyst is infected?
An infected sebaceous cyst may show signs such as:
-
Redness and warmth around the cyst
-
Tenderness or pain
-
Pus or an unpleasant-smelling fluid draining from the cyst
-
Swelling or a hard lump around the cyst
5. Can I pop a sebaceous cyst myself?
It is not recommended to pop or squeeze a sebaceous cyst yourself. Doing so can lead to infection, scarring, or the cyst returning. If you want the cyst removed, it’s best to consult a healthcare professional.
6. Will a sebaceous cyst go away on its own?
Small sebaceous cysts sometimes resolve on their own over time, but larger ones usually do not disappear without intervention. If the cyst is causing discomfort, infection, or cosmetic concerns, a doctor may recommend drainage or surgical removal.
7. How is a sebaceous cyst treated?
Treatment options for sebaceous cysts include:
-
Draining the cyst (if infected)
-
Surgical removal (for persistent or bothersome cysts)
-
Antibiotics (if there’s an infection)
8. Can sebaceous cysts be removed at home?
No, sebaceous cyst removal should be done by a medical professional. Removing it at home can lead to infection and scarring. A doctor can remove the cyst safely in a sterile environment.
9. How long does it take to heal after a sebaceous cyst is removed?
Healing time can vary depending on the size and location of the cyst. After a minor procedure, most people heal within 1 to 2 weeks. If the cyst was larger or needed stitches, healing may take longer, and proper wound care is essential to avoid infection.
10. Are sebaceous cysts related to acne?
While sebaceous cysts and acne both involve clogged pores, they are different. Acne typically involves inflammation and infection in the pores, while sebaceous cysts are non-inflammatory and typically painless unless infected.
11. Can sebaceous cysts come back after removal?
Yes, sebaceous cysts can sometimes come back, especially if the entire cyst wall wasn’t removed during surgery. If a small piece of the cyst wall remains, the cyst may regrow. Complete removal is often necessary to prevent recurrence.
12. Can a sebaceous cyst turn into cancer?
Sebaceous cysts are usually benign, but in very rare cases, they can be mistaken for or evolve into more serious conditions. If a cyst changes in size, color, or texture, it should be evaluated by a doctor to rule out malignancy.
13. Are sebaceous cysts more common in certain areas of the body?
Sebaceous cysts can appear anywhere on the body but are most common on the face, neck, and back, where sebaceous glands are more abundant.
14. Are sebaceous cysts hereditary?
Yes, sebaceous cysts can be hereditary. If someone in your family has had cysts, you may be more likely to develop them. Certain genetic conditions, such as Gardner’s syndrome, can also increase the risk of developing multiple cysts.
15. Should I see a doctor for a sebaceous cyst?
You should see a doctor if:
-
The cyst becomes painful, inflamed, or infected
-
The cyst grows rapidly or shows changes in appearance
-
The cyst is located in a sensitive area (e.g., face, genitals)
-
You want to have the cyst removed for cosmetic or practical reasons
16. Can sebaceous cysts occur on the scalp?
Yes, sebaceous cysts can form on the scalp. These cysts are often hard to notice, but they can be felt as small lumps under the skin. They can sometimes cause discomfort if they become inflamed or infected.
17. Is there a way to prevent sebaceous cysts?
While you can’t always prevent sebaceous cysts, keeping your skin clean and avoiding skin trauma can help reduce the likelihood of developing them. Regular washing and exfoliating can also help prevent clogged pores, which are a common cause of sebaceous cysts.
18. Can sebaceous cysts be drained at home?
Draining a sebaceous cyst at home is not recommended. If done improperly, it can lead to infection, worsen the cyst, or cause scarring. It’s always better to have a professional evaluate and drain the cyst if necessary.