A kidney transplant is the preferred treatment for end‑stage renal disease, offering freedom from lifelong dialysis and improved quality of life. In recent years, India has gained recognition as a premier destination for kidney transplantation. Patients benefit from highly skilled surgeons, internationally accredited hospitals, and costs that are 60–80% lower than in Western countries. According to DivinHeal’s blog “Kidney Transplant in India: Cost, Procedure & Success Rate”, India’s transplant ecosystem combines clinical excellence with affordability and streamlined care pathways for both domestic and international patients.
Understanding Kidney Transplantation
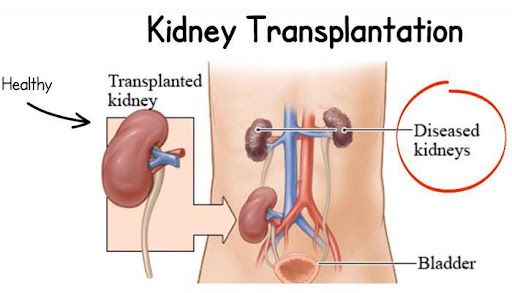
A kidney transplant replaces a failing kidney with a healthy one from either a living or deceased donor. Benefits include:
-
Improved Survival: Transplant recipients have higher life expectancy compared to those on dialysis.
-
Enhanced Quality of Life: Freedom from dialysis sessions allows a return to normal activities, work, and travel.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: While upfront costs exist, long‑term expenses are lower compared to chronic dialysis.
Candidates typically have a glomerular filtration rate (GFR) below 20 mL/min/1.73 m² or are on dialysis. A thorough medical evaluation ensures patients can tolerate surgery and immunosuppression.
Living vs. Deceased Donor Transplants
Living Donor Transplant
A relative or friend donates one kidney. Advantages:
-
Shorter Wait Time: Transplants can be scheduled promptly.
-
Better Matching: Close human leukocyte antigen (HLA) matching reduces rejection risk.
-
Improved Graft Survival: Living donor grafts last longer on average.
Deceased Donor Transplant
Kidneys from brain‑dead donors are allocated via national registries. Benefits include:
-
Broader Donor Pool: Patients without a living donor can still receive a transplant.
-
Regulated Allocation: Systems ensure fairness based on urgency, compatibility, and wait time.
Patients should register on both living and deceased donor lists to maximize their chances.
Pre‑Transplant Evaluation
A structured workup precedes any kidney transplant:
-
Medical History & Physical Exam: Assessment of cardiovascular, pulmonary, and infectious disease risks.
-
Laboratory Tests: Blood counts, liver and kidney function, viral serologies (HIV, hepatitis), and immunological panels.
-
Imaging Studies: Ultrasound of native kidneys, chest X‑ray, and cardiac echo to evaluate overall health.
-
Donor Screening: Living donors undergo rigorous medical, psychological, and compatibility testing (blood type, HLA typing, crossmatch).
Completing these steps ensures patient safety and optimal timing of surgery.
Surgical Procedure
Transplant Day
-
Anesthesia & Incision: General anesthesia is administered. A lower abdominal incision exposes the iliac vessels.
-
Implantation: The donor kidney is placed in the iliac fossa. Surgeons connect its artery and vein to the recipient’s iliac vessels and attach the ureter to the bladder.
-
Closure & Monitoring: Incisions are closed; patients spend 24–48 hours in ICU for observation of vital signs, urine output, and early graft function.
Post‑Operative Care
-
Immunosuppression: A combination of calcineurin inhibitors (e.g., tacrolimus), antiproliferative agents (e.g., mycophenolate), and steroids prevents rejection.
-
Monitoring: Daily blood tests track kidney function (creatinine, electrolytes) and drug levels.
-
Mobilization: Patients begin gentle movement within 24 hours to reduce complications.
Cost Breakdown
India’s kidney transplant costs range from ₹500,000 to ₹1,500,000 (USD 8,600–25,800), which include:
| Item | Cost (INR) | Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Surgeon & Hospital Fees | 300,000 – 800,000 | 5,200 – 13,800 |
| Donor Evaluation & Surgery | 50,000 – 150,000 | 860 – 2,600 |
| Pre‑ and Post‑Op Care | 100,000 – 300,000 | 1,700 – 5,200 |
| Immunosuppressive Medications | 50,000 – 200,000 | 860 – 2,600 |
| Follow‑Up Visits (6 months) | 20,000 – 50,000 | 340 – 860 |
Note: Costs vary by hospital accreditation, city, and patient complexity.
Factors Influencing Cost
-
Hospital Accreditation: JCI/NABH‑accredited centers charge premium rates for advanced infrastructure.
-
Donor Type: Living donor procedures include donor workup and surgery costs; deceased donor cases involve organ procurement charges.
-
Patient Condition: Comorbidities (cardiac, pulmonary) may require extended ICU care.
-
Medication Regimen: Newer immunosuppressants can be more expensive but offer improved side‑effect profiles.
-
Length of Stay: Standard stay is 7–10 days; complications extend hospitalization and increase costs.
Success Rates & Outcomes
India’s transplant success rates rival global benchmarks:
-
One‑Year Graft Survival: 90–95%
-
Five‑Year Graft Survival: 80–85%
-
Ten‑Year Graft Survival: 60–70%
Long-term outcomes depend on strict adherence to medication, regular monitoring, and lifestyle modifications (diet, exercise, infection prevention).
Patient Journey & Experience
-
Initial Consultation: Virtual reviews allow overseas patients to submit medical records and obtain a preliminary plan.
-
Travel & Admission: Facilitators arrange hospital appointments, visa support, and accommodation near the facility.
-
Transplant & Early Recovery: Focus on graft function, wound healing, and initiation of immunosuppression.
-
Discharge & Home Care: Detailed instructions on medication, diet, hygiene, and emergency contact procedures.
-
Long‑Term Follow‑Up: Regular visits every 1–3 months for the first year, then biannually, to monitor graft health.
Dedicated transplant coordinators guide patients through each step, ensuring coordination and support.
Conclusion
Choosing a kidney transplant in India represents far more than a cost‑effective medical decision—it’s an investment in your long‑term health, independence, and quality of life. With survival rates matching or exceeding global standards, Indian transplant centers offer:
-
Expertise and Experience: Renowned surgeons with extensive fellowship training and multidisciplinary teams ensure that every step—from donor selection to post‑operative care—is handled with precision and compassion.
-
State‑of‑the‑Art Facilities: JCI and NABH‑accredited hospitals feature advanced operating theaters, on‑site laboratories, and dedicated transplant units designed to minimize complications and support rapid recovery.
-
Comprehensive Support: From your first virtual consultation through visa assistance, accommodation arrangements, and seamless coordination of follow‑up appointments, specialized transplant coordinators guide you and your family at every turn.
-
Personalized Care Plans: Recognizing that each patient’s journey is unique, Indian centers tailor immunosuppression regimens, dietary counseling, and rehabilitation protocols to your specific needs and lifestyle goals.
-
Affordability Without Compromise: By dramatically reducing the financial burden—often by 60–80% compared to Western nations—India unlocks access to life‑saving treatment while allowing you to allocate resources toward long‑term wellness and family support.
Ultimately, a kidney transplant in India offers not just a new organ, but a renewed lease on life—free from the constraints of dialysis, empowered by restored health, and supported by a global community of medical excellence. If you or a loved one is facing end‑stage renal disease, exploring India’s transplant options could transform uncertainty into hope, enabling you to embrace the future with confidence and vitality.